Zambia Population and Language
Zambia is a country with more than 70 different groups of people and about as many languages. Nearly half of the population lives in the so-called line of rail, which extends along the railway line from the town of Livingstone in the south via the capital Lusaka to the province of the Copperbelt in the north, where the country’s copper mines are located. The rest of the country is sparsely populated countryside.
The seven largest ethnic groups are Bantu people – Bemba, Nyanja, Tonga, Lozi, Luvale, Lunda and Kaonde. These groups are represented in all ten provinces of Zambia, and they are difficult to clearly distinguish from one another. Languages also overlap, and on the boundaries between their core areas there are a number of linguistic intermediate forms.
- COUNTRYAAH.COM: Key populations estimated size and data of Zambia, including population density of how many people per square mile. Also included are facts for population and language.
It is of some political significance what ethnic affiliation a person has, since several political parties are dominated by a people group. But unlike other countries in the region, there are no serious contradictions between the groups. Among the lozi that dominate in the west, there is a separatist movement, but it uses peaceful methods (see Modern History).
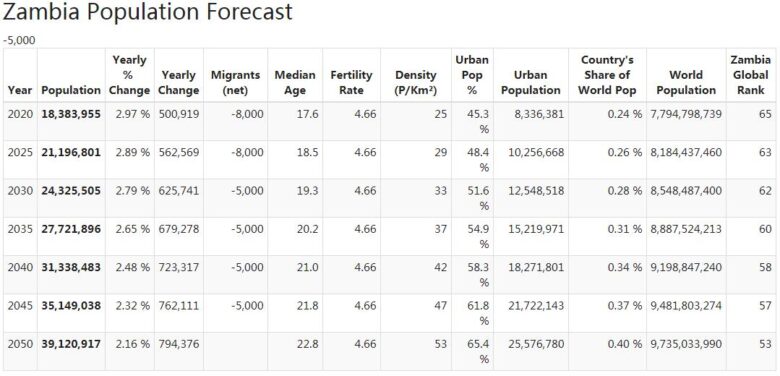
Rapid population increase
The country has a minority of Zambians of European descent, mainly from the United Kingdom and South Africa. A small but economically strong group are the Asians, most of whom are from India. In recent years, residents of Chinese origin have become more numerous.
Zambia has received many refugees from war-torn neighboring countries. In 2018, according to the UN, Zambia housed approximately 33,000 refugees from Congo-Kinshasa.
The population is increasing rapidly, although the rate of increase has slowed since the mid-1990s. In 2015, almost half of the population was under 15. The HIV / AIDS epidemic has hit the country hard (see Social conditions). Nowadays, however, more and more HIV-infected brake medications are receiving and the death rates that can be directly linked to HIV / AIDS are decreasing, as is the number of cases where the HIV virus has been transmitted from mother to child, according to the Zambian health authorities in 2014.
All of the country’s major cities are located along the railroad which, since independence in 1964, has attracted large numbers of people with relatively well-paid jobs in both government administration and in mines and industries. Moving into the cities has created major problems in the form of unemployment, housing shortages and growing slums.
Eight languages with official status
At independence from Britain, the former colonial language was made English as the official language. It is now used in the public administration and the business sector. In addition, all major newspapers and magazines are published in English. Still, only a minority of the population can be said to master the language. Most Zambians speak some of the local languages instead, of which the languages of the seven largest peoples have official status.
Bemba is the largest local language and is spoken mainly in the north, including in the Copperbelt. Tonga is spoken mainly in the south, while lozi is used in the south and west. Nyanja dominates in the east. Only a tenth of Zambians have a new mother tongue, yet they have a dominant role as the main language in the capital Lusaka. Nyanja has also been the language of the police and the army since the colonial era and is also the official language of Malawi, where it is called chewa.
Most Zambians speak more than one language, but their mother tongue is often important for ethnic identity.
FACTS – POPULATION AND LANGUAGE
Population
over 70 bantu people of which bemba, nyanja and tonga are the largest 1
Number of residents
17 094 130 (2017)
Number of residents per square kilometer
23 (2017)
Percentage of residents in the cities
43.0 percent (2017)
Nativity / birth
38.1 per 1000 residents (2016)
Mortality / mortality
7.8 per 1000 residents (2016)
POPULATION GROWTH
3.0 percent (2017)
fertility rate
5.0 number of births per woman (2016)
Percentage of women
50.4 percent (2017)
Life expectancy
62 years (2016)
Life expectancy for women
64 years (2016)
Life expectancy for men
59 years (2016)
Language
official language is English 2
- small minorities of whites and Asians
2. seven bantu languages have official status (bemba, nyanja, tonga, lozi, luvale, lunda and kaonde)
2009
August
Court free Chiluba
A Zambian court acquits Chiluba of charges of corruption. The Court notes that while the President spent large sums of money, it does not prove that the money came from the Treasury.
May
Splits within PF
Sata announces that he is running for PF in the December 2011 presidential election, causing a quarrel with his rivals within the party.
March
No to a conversion
The Supreme Court rejects PF leader Sata’s demand for a recalculation of the votes in the 2008 elections.
The ex-president’s wife is sentenced
President Chiluba’s wife Regina is sentenced to several years in prison for receiving stolen state property.